Alternative ways to import data
Prior to version 3.x there are two ways to import data into the central repository from remote instances SQL Server Integration Package (SSIS) and Linked Server.
Adding remote server to collection
In both cases, the configuration of the remote instance is the same. For the central repository to know which remote instances to collect data from, they must be defined in [dbo].[sqlwatch_config_sql_instance]. This can be achieved by directly inserting data into the table, or by executing a stored procedure:

exec [dbo].[usp_sqlwatch_config_repository_add_remote_instance]
@sql_instance --sql instance name,
@hostname --hostname, if different to the @sql_instance, for example this could be in IP if no DNS records present,
@sql_port --non standard sql port, leave NULL for the default 1433,
@sqlwatch_database_name --name of the SQLWATCH database,
@environment --name of the environment (DEV,PROD,QA or anything) - this is for the user convinience,
@linked_server_name --name of the linked server, a new LS will be created if not exists. If you prefer to use existing LS, leave this blank and manually update [linked_server_name] in [dbo].[sqlwatch_config_sql_instance]. If you are using SSIS, leave NULL.
@rmtuser --username for the linked server authentication, leave NULL for default Windows Auth or when using SSIS,
@rmtpassword --password for the linked server authentication, leave NULL for default Windows Auth or when using SSIS,
SQL Server Integration Services Package
It is assumed that the SQL Server Integration Package (SSIS) is installed and configured and that the SSISDB has been initialized and the environment is operational.
Package Deployment
The SSIS package can be easily deployed using the provided .ispac file. Learn more about SSIS deployment. Alternatively, it can be also deployed from the Visual Studio Project. Upgrading SSIS package is simply re-deploying a newer version and removal is done by deleting the deployed package.
Package Configuration
To configure SSIS package, navigate to the Project in the Integration Services Catalogs: 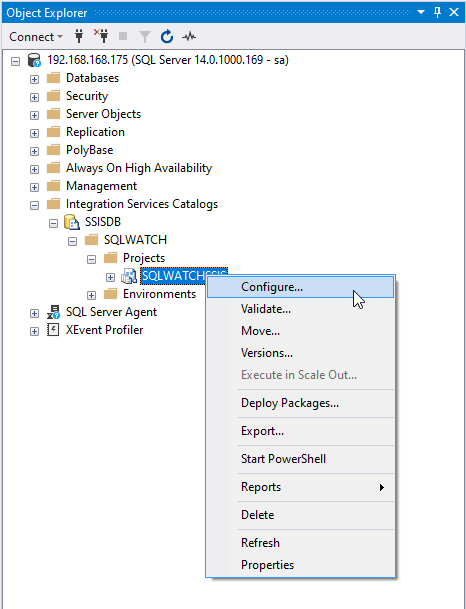
You can apply the configuration to the project, or individual packages. The project will contain the collection of all configuration options from child packages. Learn more about SSIS Catalog
Control Package
The control package control_import.dtsx is responsible for orchestrating multi-threaded data collection and execution of the Worker Package import_remote_data.dtsx 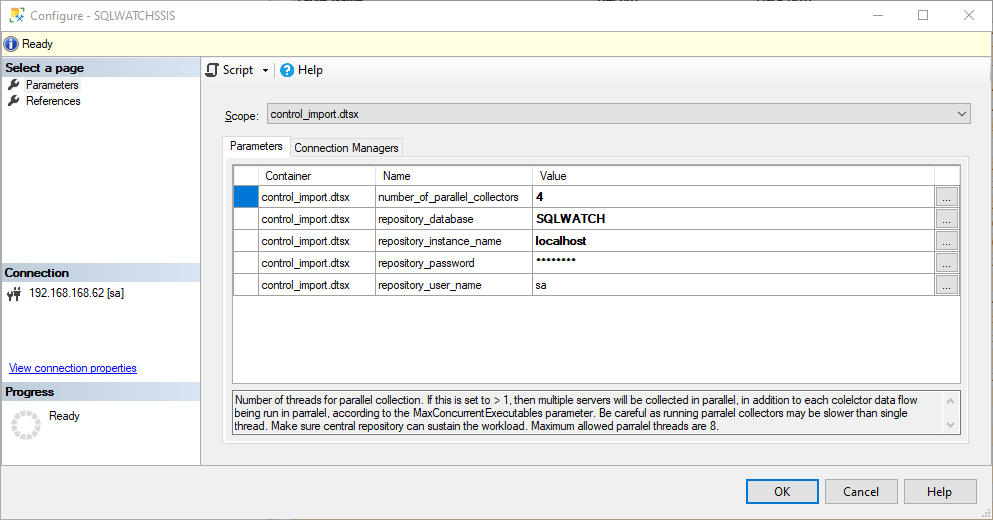
Parameters
number_of_parallel_collectors: The number of threads for parallel collection. If this is set to > 1, then multiple servers will be collected in parallel, in addition to each collector data flow being run in parallel, according to the MaxConcurrentExecutables parameter. Be careful as running parallel collectors may be slower than a single thread. Make sure the central repository can sustain the workload. Maximum allowed parallel threads are 8.
repository_database: The name of the database where the central repository is. Default SQLWATCH.
repository_instance_name: The name of the SQL Server instance where the central repository is hosted.
repository_password: The SQL Password to access central repository or blank for Windows authentication.
repository_user_name: The SQL User to access central repository or blank for Windows authentication.
Worker Package
The worker package import_remote_data.dtsx is responsible for the actual data collection from remote instances into the central repository. 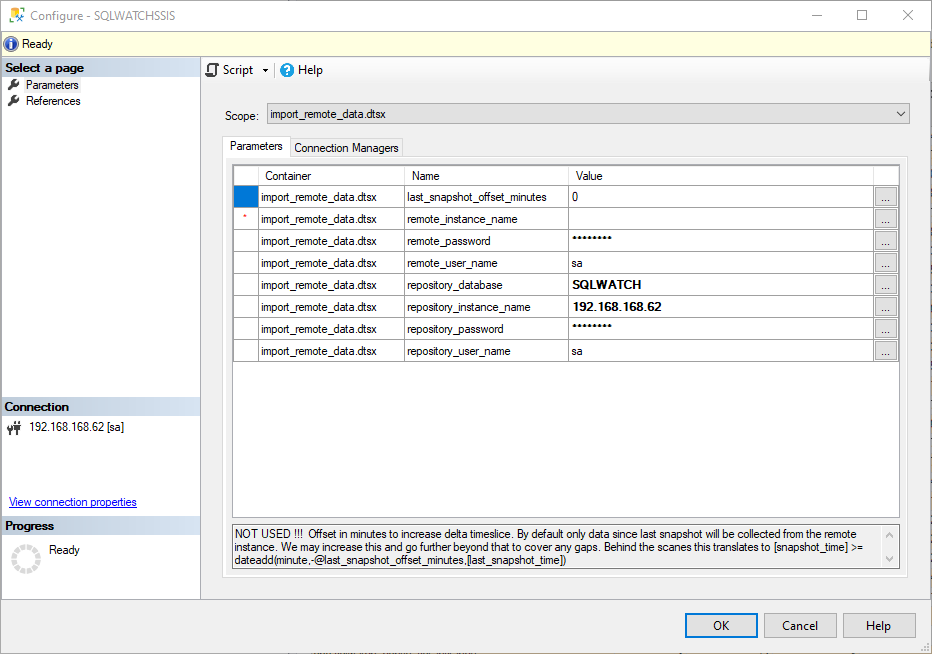
Parameters
Worker package parameters are passed from the control package. However, you can also invoke the worker package manually for a specific instance with the same parameters
last_snapshot_offset_minutes (NOT USED): Offset in minutes to increase delta time slice. By default, only data since the last snapshot will be collected from the remote instance. We may increase this and go further beyond that to cover any gaps. Behind the scenes this translates to [snapshot_time] > dateadd(minute,-@last_snapshot_offset_minutes,[last_snapshot_time])
remote_instance_name: SQL Instance to collect data from. This parameter is passed from the control package during run time.
remote_password: SQL Password for the remote instance or blank for Windows authentication.
remote_user_name: SQL User for the remote instance or blank for Windows authentication.
In the current implementation, it is not possible to specify different accounts for accessing remote instances. This means that when using SQL Authentication all instances must have the same SQL User and Password. When using Windows authentication this is usually not a problem as the SSIS runs under a context of one the SQL agent or proxy account
repository_database The name of the database where the central repository is. Default SQLWATCH.
repository_instance_name The name of the SQL Server instance where the central repository is hosted.
repository_password The SQL Password to access central repository or blank for Windows authentication.
repository_user_name The SQL User to access central repository or blank for Windows authentication.
Execution
The package does delta loads of the logger* tables and full loads of the meta* tables. Meta tables are relatively small and should not contain more than a few hundred rows. Logger tables can be quite big and thanks to delta loads, the more often the package runs, the less data it pulls with every run. A good start is to run it every 10 minutes.
There is no predefined agent job for the SSIS based repository collector due to a variety of environments and folder names in SSISDB. Once the package has been deployed onto the preferred Integration Services Server and configured please crate agent job with the schedule as you please.
When scheduling the .dtsx, the control package should be called from the agent job: 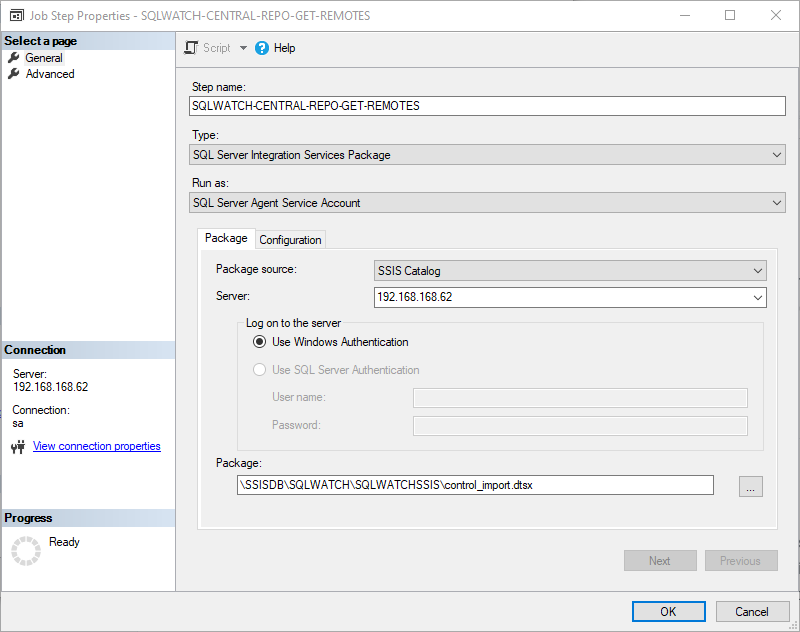
Linked Server
In order to invoke collection via Linked Server, a linked server object to the SQLWATCH database on each monitored instance must be created. This can be achieved by executing stored procedure [dbo].[usp_sqlwatch_user_repository_create_linked_server]
Create all required linked servers
The procedure can create all required linked servers as per the [linked_server_name] column in [dbo].[sqlwatch_config_sql_instance] table:
exec [dbo].[usp_sqlwatch_config_repository_create_linked_server]
@rmtuser --optional user name for the remote instance (same for all) or blank to use default windows auth,
@rmtpassword --optional password for the remote instance (same for all) or blank to use default windows auth
Create a specific linked server
Alternatively, it can create a specific linked server. This is the default behavior when executing [dbo].[usp_sqlwatch_user_repository_add_remote_instance]
exec [dbo].[usp_sqlwatch_config_repository_create_linked_server]
@sql_instance --name of the existing sql instance in [dbo].[sqlwatch_config_sql_instance],
@linked_server --optional, name of the required linked server. if blank a default name will be created,
@rmtuser --optional user name for the remote instance (same for all) or blank to use default windows auth,
@rmtpassword --optional password for the remote instance (same for all) or blank to use default windows auth
Learn more about creating Linked Servers
Create remote collector jobs
Linked Server collector can be multi-threaded and there is no limit on the number of threads providing the performance of the central repository is adequate. The linked server approach creates a table based queue of all remote objects to import with the required dependency (i.e. meta tables first, the logger tables) in [dbo].[sqlwatch_meta_repository_import_queue]. The queue can be then processed by executing stored procedure:exec [dbo].[usp_sqlwatch_repository_remote_table_import]. To increase the number of import threads schedule the above procedure multiple times. To create default repository agent jobs, please execute the below procedure:
exec [dbo].[usp_sqlwatch_config_repository_create_agent_jobs]
@threads = --number of thread jobs to create
This will result in the following jobs to be created:
- A single enqueuing job that creates a list of remote objects to pull data from ([dbo].[sqlwatch_meta_repository_import_queue]) and ultimately controls how often they are processed.
- A single or multiple import jobs, depending on the @threads variable that will process the import queue. These jobs can run every 1 minute and will process any outstanding items in the queue table.
SQLWATCH-REPOSITORY-IMPORT-ENQUEUE
SQLWATCH-REPOSITORY-IMPORT-T2
SQLWATCH-REPOSITORY-IMPORT-T3
SQLWATCH-REPOSITORY-IMPORT-T4
SQLWATCH-REPOSITORY-IMPORT-T5
SQLWATCH-REPOSITORY-IMPORT-T6
SQLWATCH-REPOSITORY-IMPORT-T7
SQLWATCH-REPOSITORY-IMPORT-T8
Execution
Each thread registers itself in the threads table [dbo].[sqlwatch_meta_repository_import_thread] which contains the name of the SQL Agent Job currently running the thread. When the thread completes, it is also removed from the threads table.
Import status of each object can be seen in the ‘[dbo].[sqlwatch_meta_repository_import_status]’ table.